Planting Atlantic White Cedar
A decade-long partnership is returning native Atlantic white cedar to Maryland's Eastern Shore.
Spring weather in Maryland is unpredictable, but on a Thursday morning in late March, the sun is shining and the birds are chirping as middle school students plant Atlantic white cedar seedlings at The Nature Conservancy’s Nassawango Creek Preserve.
Why are the students planting Atlantic white cedar trees? Why are they doing so at this particular nature preserve? And how did middle schools in Worcester, Wicomico and Somerset County acquire these trees in the first place? To answer these questions, let’s go back to 2009 when an unanticipated, yet very fruitful, partnership between the National Aquarium and TNC began.

A Conservation Partnership Is Formed
The National Aquarium is home to a diverse cast of underwater creatures. Yet most people might not realize that this non-profit organization excels at connecting people to nature and teaching youth the importance of conservation. In fact, the National Aquarium’s mission is to inspire conservation of the world’s aquatic treasures.
While outreach and education are core tenets of the National Aquarium, land acquisition is not. TNC’s Maryland/DC chapter has helped protect more than 75,000 acres of land and owns 31 nature preserves in Maryland. These were the enabling conditions for a partnership that started in 2009 and has continued to thrive ever since.
In 2009, the National Aquarium acquired thousands of Atlantic white cedar seedlings in an effort to restore this native species and its habitat. Cedar swamps were once found throughout the Gulf and Atlantic coasts but centuries of development and land conversion have reduced these habitats to a fraction of their original range. Cedar swamps are home to a host of plants and animals and provide ecosystem services for people including water filtration.
After being approached by the Aquarium, a middle school on the Eastern Shore agreed to add the tree planting to the students’ curriculum as a field trip. Everything seemed to be in place until the planting site that the Aquarium had secured fell through at the last minute.
The Aquarium was left with trees to plant and kids to plant them, but with nowhere to actually plant the trees.
TNC heard about the Aquarium’s dilemma shortly after completing a project to restore the hydrology at a section of Nassawango Creek Preserve, which was done in anticipation of a cedar restoration plan. The timing was perfect. The Aquarium now had a place to plant trees with students and TNC now had trees to go in the ground.
A restoration partnership, now 10 years in the making, commenced.

A Signature Species: Atlantic White Cedar
Atlantic white cedar (AWC) trees are actually a member of the cypress family. These tall evergreens reside in swamps, marshes and other wet regions of the mid-Atlantic. Given that the straight-grained wood from these trees is light, buoyant and resistant to decay, Atlantic white cedars have been heavily logged since European colonization. In the 1700s, Atlantic white cedars were utilized for ship-building, shingles, charcoal, barrels and more.
But humans are not the sole beneficiary of Atlantic white cedars. This tree species provides cover and food to a variety of insects, birds and mammals. The yellow-throated warbler nests in Atlantic white cedar swamps while white-tailed deer are particularly fond of the tree’s tasty foliage. These majestic trees can live up to 1,000 years when their habitats are undisturbed.
Given the importance of these trees for both people and nature, TNC and the National Aquarium have worked together for more than a decade to return this native species to the region at a scale that will endure far into the future. However, restoring Atlantic white cedar is much more than just planting trees. It requires a restoration of the habitat conditions that the tree needs to thrive.
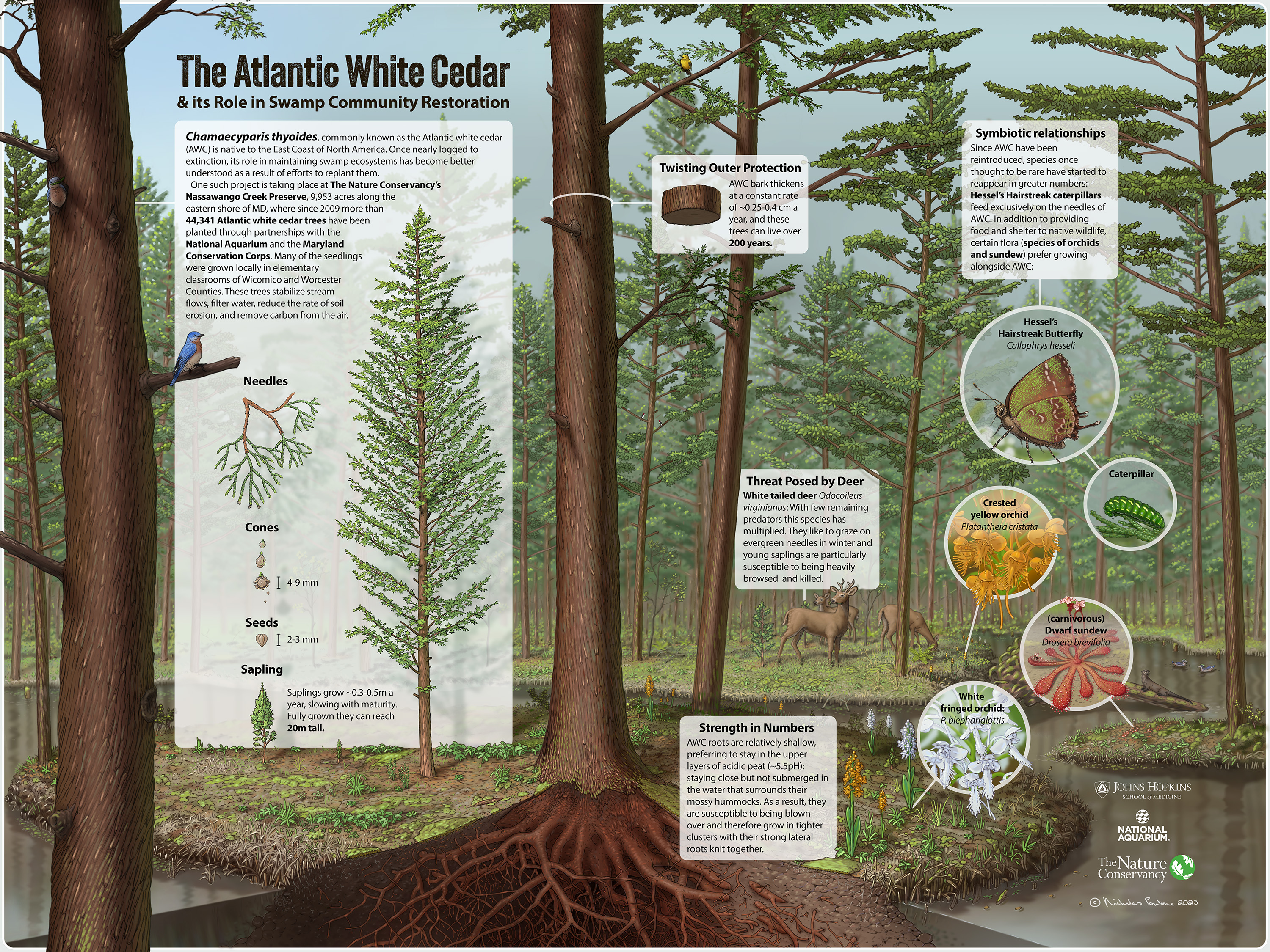
Atlantic White Cedar (AWC) Swamp Community
Once nearly logged to extinction, Atlantic white cedar's role in maintaining swamp ecosystems has become better understood as a result of efforts to replant them. These trees stabilize stream flows, filter water, reduce the rate of soil erosion and remove carbon from the air.
Restoration Efforts
Since 2009 more than 44,341 Atlantic white cedar (AWC) trees have been planted at Nassawango Creek Preserve through partnerships with the National Aquarium and the Maryland Conservation Corps. These trees stabilize stream flows, filter water, reduce the rate of soil erosion and remove carbon from the air.
Twisting Outer Protection
AWC bark thickens at a constant rate of ~ 0.25 - 0.4 cm a year, and these trees can live for more than 200 years.
Threat Posed by Deer
With few remaining predators, white-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus) have multiplied. They like to graze on evergreen needles in winter, and young saplings are particularly susceptible to being heavily browsed and killed.
Strength in Numbers
AWC roots are relatively shallow, preferring to stay in the upper layers of acidic peat (~ 5.5 pH), staying close but not submerged in the water that surrounds their moss hummocks. As a result, they are susceptible to being blown over and therefore grow in tighter clusters with their strong lateral roots knit together.
Symbiotic Relationships
Since AWC have been reintroduced, species once thought to be rare have started to reappear in greater numbers. Hessel's hairstreak caterpillars feed exclusively on the needles of AWC. In addition to providing food and shelter to native wildlife, certain flora including species of orchids and sundew prefer growing alongside AWC.

True Wilderness: Nassawango Creek Preserve
Nassawango Creek Preserve is one of the few areas of true wilderness left on the Eastern Shore. Characterized by bald cypress and black gum, the massive trees of this primeval forest envelop canoeing and kayaking visitors with ample shade and security.
What started as a gift of 154 acres in 1978 by local residents hoping to maintain this natural wonder has since grown tremendously. Through years of dedication and partnerships, TNC has worked to protect 14,787 acres of swamp and upland forest along Nassawango Creek. Today, the preserve includes 9,953 acres of land and is one of the northernmost remaining examples of a bald cypress swamp.
Some parts of Nassawango Creek Preserve retain their native beauty, yet other portions of land on the preserve were altered decades ago and no longer resemble a cedar swamp. Over the past century, large areas of the now-preserve were drained to make room for the fast-growing loblolly pine, a tree that is extensively cultivated in forest plantations for pulpwood and lumber.
It will take time to convert the loblolly pine plantations back into a swamp, but the payoff from this effort includes improving the overall health and biodiversity of Nassawango Creek and providing the majestic Atlantic white cedar a chance to make a comeback.

In the summer of 2007, TNC began restoring degraded parts of Nassawango Creek Preserve by following a three-step process:
STEP 1: Identify, Harvest, Prep. Loblolly stands that have been drained for timber production and located adjacent to the unaltered mature cedar swamps are selected as suitable sites for restoration. The loblolly pines on these sites are then harvested. Once cleared, the fields are prepared with a controlled burn.
STEP 2: Restore Hydrology. Before the preserve was protected, timber harvesting operations ditched the land to drain water more rapidly into nearby Nassawango Creek so that the pines could grow more rapidly. To restore the hydrology of the site, ditch plugs, rock weirs and other techniques are used to convert the unnatural surface water system back to a groundwater system. Once this step is completed, water seeps into the soil creating wetland conditions, rather than rapidly draining off the land.
STEP 3: Plant Trees. For more than 10 years, TNC, the National Aquarium and Worcester, Wicomico and Somerset County middle school students have planted more than 37,000 trees at Nassawango Creek Preserve. Bringing back the iconic Atlantic white cedar trees after centuries of disruption is the final step in the process to restore a native ecosystem.

A Lesson in Nature
On a March morning, students from Snow Hill Middle School descend upon Nassawango Creek Preserve to plant trees. Some are eager to share their thoughts on the tree planting day. While handling a dibble bar—a tool used by foresters to plant seedlings— a student named Josh explains simply, “I love being outdoors.”
Admiring the landscape, another student named Sloan states, “compared to the classroom, the planting is more of an interactive learning experience.” Katalina mentions eagerly, “the day is kind of like an adventure.”
Angela Landreth, a 20-year teaching veteran at Snow Hill Middle, observes, “Having the kids outside shows you a totally different side of them. I’m seeing partnerships that I wouldn’t see in the classroom. Kids that wouldn’t work well together academically are putting in good work here.” Angela then explained how the students kept the potted seedlings growing at their school for a full year before bringing them to the preserve to be planted: “It’s been nice for the kids to see the full process. They’re so excited.”
Quote: Angela Landreth, Snow Hill Middle School
Having the kids outside shows you a totally different side of them. I’m seeing partnerships that I wouldn’t see in the classroom. Kids that wouldn’t work well together academically are putting in good work here.

Bringing Back an Icon
Cedar swamps provide countless benefits to both people and nature. Healthy conifer forests help regulate temperatures year-round, so part of the goal in restoring these forests is to make the region more resilient in the face of climate change.
Cedar swamps can also help regulate the region’s soil hydrology by keeping the land wetter during dry periods and by storing water during wet periods. There is a growing body of scientific evidence, including studies led by TNC, that have quantified the benefits of harnessing nature as a strategy for tackling climate change while providing added benefits to people, water and wildlife.
Bringing Atlantic white cedar swamps back to Maryland is part of that strategy, and watching young people participate in the process gives us hope for a future where people and nature thrive together.
How You Can Help
Seventh graders aren't the only ones who have the opportunity to plant Atlantic white cedar at Nassawango Creek Preserve. Each year there is a planting day in late March reserved for all volunteers. Sign up for our Nature News e-newsletter to get updates about this and other opportunities across Maryland and DC.